Forging Heat Treatment: How Does It Help In CNC Machining Services?
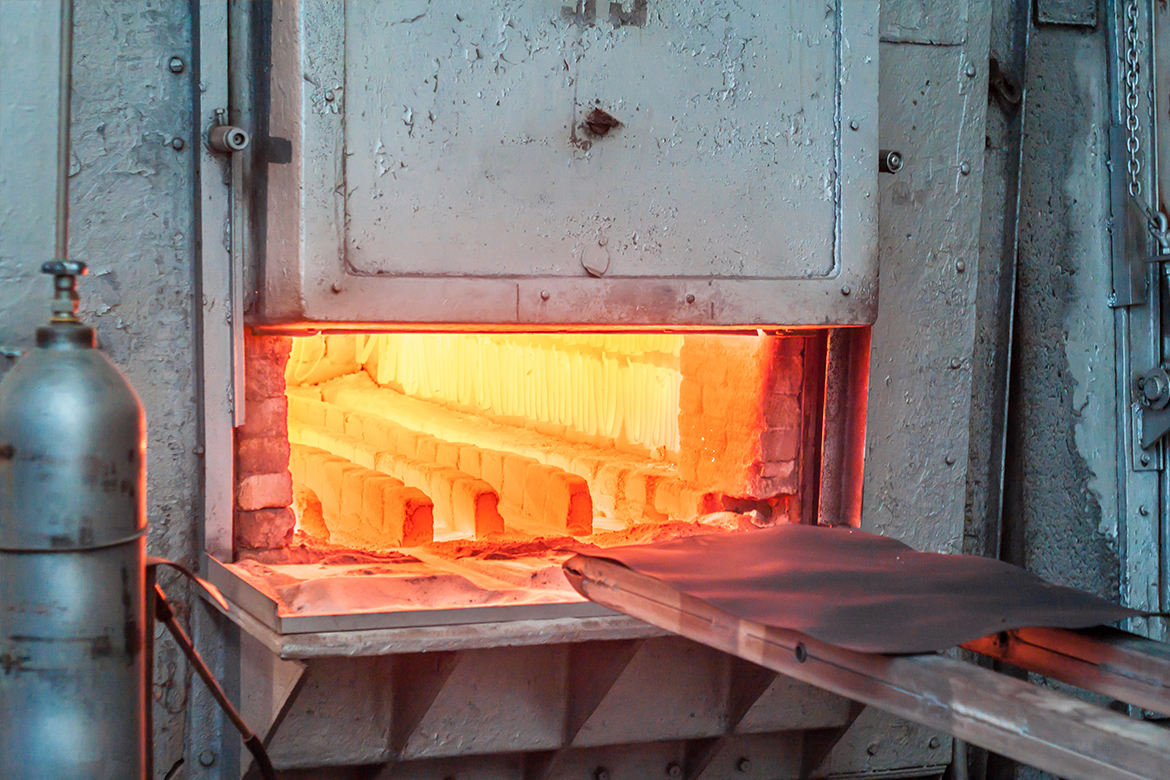
Among the critical value-added products offered by the provider for steel forgings is forging heat treatment. This post-treatment modifies the mechanical properties of items to enhance their working efficiency. Most steel forgings could be heat treated after forging. Furthermore, heat treatment is essential in closed die forging for producing desired features, including grain structural development, stress alleviation, and improved mechanical and physical properties. Furthermore, steel forgings can be quenched or tempered to provide the desired final properties. Let’s discover more about forging heat treatment.
What Is Forging Heat Treatment?
Some aluminium alloys are not heat-treatable, but those that are may be treated in a variety of ways. A certified provider utilises specialised equipment to offer the precise heat control necessary for outstanding results with aluminium alloys. Forging heat treatment entails heating metal alloys to severe degrees, accompanied by a regulated cooling procedure. The temperature to which the material is then heated, the time spent at that temperature, and the pace at which it is cooled all have a substantial influence on the final physical attributes of the metallic alloy.
In addition, metal alloys may benefit from heat treatments to increase essential physical qualities such as machinability, strength, and hardness. These modifications occur as a result of changes in the microstructure and, in some instances, the chemical content of the material.
What Are The Different Heat Treatment Methods?
Several of the most prevalent forging heat treatment techniques are as follows:
Normalising
It entails heating the forging to a particular degree and then allowing it to cool in an environment with no mobility. As a consequence, flexibility has been regained. In addition, normalised forgings are less expensive than wholly annealed forgings since, ultimately, annealing necessitates furnace-controlled cooling.
Annealing Procedure
This material could be used in low-carbon steel forgings. The forging is permitted to cool in perfectly still air after being treated to a reduced temperature than in annealing or full normalising. This changes the grain size in addition to the flow of the forging.
Full Annealing
Forging restores the metal’s elasticity, ensuring that the forging maintains a constant amount of softness along its entire length. It should be warmed to a specified temperature before being chilled at regular intervals inside a furnace.
Quenching And Tempering
After cooling, the metal forging is warmed at temperatures of 400 to 600°C. Tempering produces a forging with the perfect balance of strength and flexibility for its particular purpose.
Spheroidizing
This metal is primarily the result of forgings of high-carbon tool steel, alloy steel, and steel. Spheroids are produced across the forging framework during the technique, boosting machinability. Furthermore, quenching and tempering are the two most common types of heat treatment. They may effectively increase the hardness of steel forgings, increasing strength for increased wear tolerance at a low cost.
What Is CNC Machining Services Forging Heat Treatment?
Heat treatment, an essential element in CNC machining metal components, is the regulated cooling and heating of a material to produce specific material characteristics. It modifies four critical material attributes of metal components: ductility, toughness, strength, and hardness. Select the best heat treatment technique depending on the material properties, component size, and desired final material attributes. Heat treatment aims to establish a specific microstructure that confers material attributes on your items.
When Is It Necessary To Use Forging Heat Treatments On Metal Parts?
Heat treatments may be applied to metal alloys at numerous phases of the CNC machining services procedure, either before or after the components are machined.
Before Using CNC Machining Services
Whenever a standardised quality of a widely accessible metal alloy is specified, the CNC network operator will manufacture the components straight from that stock material. This is frequently the most excellent solution for shortening lead times.
After CNC Machining Services
Various heat treatments improve the hardness of the material substantially or are employed as a final phase after forming. Heat treatment is used after CNC machining because excessive hardness affects a material’s machinability. For instance, this is a typical procedure in CNC machining tool steel pieces.
What Are The Benefits Of Forging Heat Treatment In Many Industries?
The demand for forging heat treatment is steadily expanding. From gears and pistons to wheel spindles, forged items are used in the aerospace, defence, and maritime industries. Furthermore, heat-treated forgings are suitable for various industrial purposes since they offer a solid yet lightweight metal for speed and energy savings. Manufacturers require these features to produce high-quality items, and heat-treated aluminium helps them do so more cost-effectively.
Other advantages might include the following:
- Resistant to rust.
- Excellent surface polish.
- High Thermal conductivity.
- Lightweight and low-density.
- The ability to freeze.
- Excellent strength-to-weight ratio.
- Designing adaptability.
Conclusion
Forging heat treatment provides approximately $15 billion in value to metal goods annually by providing attributes required for parts to function correctly. It is intrinsically linked to the manufacture of steel products: steel accounts for approximately 80% of heat-treated parts. It’s also an essential step in the production of nonferrous commodities. Forging heat treatment, for example, improves the durability and hardness of aluminium alloy vehicle castings, just as heat treatment improves the durability and hardness of heat treatment. Forging heat treatment is the procedure of heating and altering the properties of steel forgings, including alloy steel.