The Role of Packaging in Hazardous Materials Management
Packaging plays a crucial role in the management of hazardous materials. Hazardous materials are substances or materials that pose a risk to human health, safety, or the environment. They include chemicals, biological agents, radioactive materials, and other substances that can cause harm if not handled properly. It is essential in the transportation, storage, and disposal of hazardous materials.
Packaging Regulations and Standards
Packaging regulations and standards are designed to ensure the safe transportation, storage, and disposal of hazardous materials. These regulations specify the types of packaging that can be used for different hazardous materials, and the requirements for labeling, marking, and documentation.
The regulations also require that packaging be tested to ensure that it is strong enough to withstand the hazards associated with the material being transported.
The United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods is the primary international standard for the transportation of hazardous materials. The standard specifies the requirements for packaging, labeling, and documentation of hazardous materials. In addition to the UN standard, there are also regional and national regulations that apply to the transportation of hazardous materials.
Types of Hazardous Materials Packaging
There are several types of dangerous goods packaging that can be used for hazardous materials, including drums, intermediate bulk containers (IBCs), and flexible intermediate bulk containers (FIBCs). Drums are the most common type of packaging used for hazardous materials. They are typically made of steel or plastic and are designed to withstand the hazards associated with the material being transported.
IBCs are larger containers that are used for the transportation and storage of hazardous materials. They are typically made of plastic or metal and are designed to be stacked for efficient storage. FIBCs are flexible containers that are used for the transportation and storage of dry bulk materials. They are typically made of woven polypropylene and are designed to be lightweight and easy to handle.
Packaging Testing and Certification
Packaging for hazardous materials must be tested and certified to ensure that it is strong enough to withstand the hazards associated with the material being transported. The testing of hazardous materials packaging includes drop testing, vibration testing, and stacking testing. These tests are designed to simulate the hazards that the packaging will be exposed to during transportation and storage.
Also, dangerous goods packaging certification is also an important part of hazardous materials management. Certification ensures that the packaging meets the regulatory requirements for the transportation, storage, and disposal of hazardous materials.
Certification is typically done by a third-party certification body and involves a review of the packaging design, materials, and testing results. Once the packaging is certified, it is marked with a certification logo and can be used for the transportation and storage of hazardous materials.
Packaging Design Considerations
When designing packaging for hazardous materials, several factors must be considered, including the type of material being transported, the hazards associated with the material, and the transportation mode. For example, packaging for radioactive materials must be designed to prevent the release of radioactive particles, while packaging for corrosive materials must be designed to prevent leaks.
Packaging design must also take into account the environmental impact of the packaging itself. For example, plastic packaging can have a significant environmental impact if not disposed of properly. Therefore, packaging designers must consider the environmental impact of the packaging materials and design packaging that is recyclable or biodegradable.
Packaging Labels and Markings
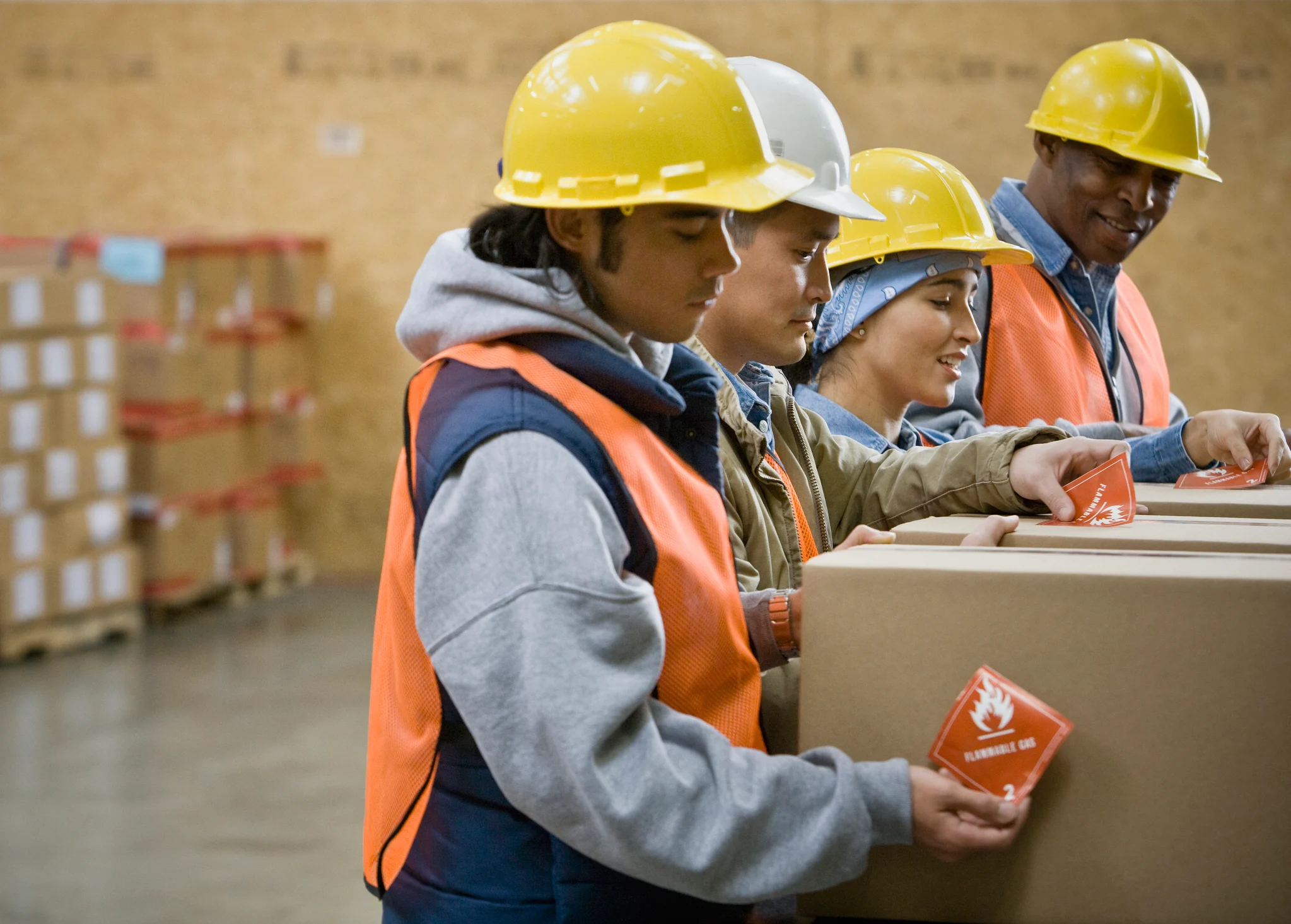
Packaging labels and markings are essential for the safe transportation and storage of hazardous materials. Labels and markings provide information about the type of material being transported, the hazards associated with the material, and the regulatory requirements for the transportation and storage of the material.
Labels and markings must be visible and legible and must meet the regulatory requirements for size, color, and placement. For example, labels for flammable materials must be red and have a black border, while labels for corrosive materials must be white and have a black border.
Conclusion
In summary, packaging is a critical component in the safe management of hazardous materials. It is essential to ensure that the right packaging is used for each type of hazardous material, and that the packaging is designed and tested to withstand the hazards associated with the material being transported.
It’s also important to consider the environmental impact of the packaging materials and design packaging that is recyclable or biodegradable. Following these guidelines, we can ensure that hazardous materials are managed safely and responsibly, protecting both human health and the environment.
Hazardous materials can find their way into recycling, posing a danger to workers. To learn more on the dangers of radiation in waste and recycling, please see the accompanying resource.
Infographic provided by truck scales experts, Kanawha Scales & Systems